Brain waves are rhythmic patterns of electrical activity generated by the synchronized firing of neurons in the brain. These waves are produced by synchronized electrical impulses from large groups of neurons communicating with each other. Brain waves can be measured using electroencephalography (EEG), a technique that records the electrical activity of the brain through electrodes placed on the scalp.
There are several types of brain waves, each associated with different states of consciousness, cognitive processes, and mental activities.
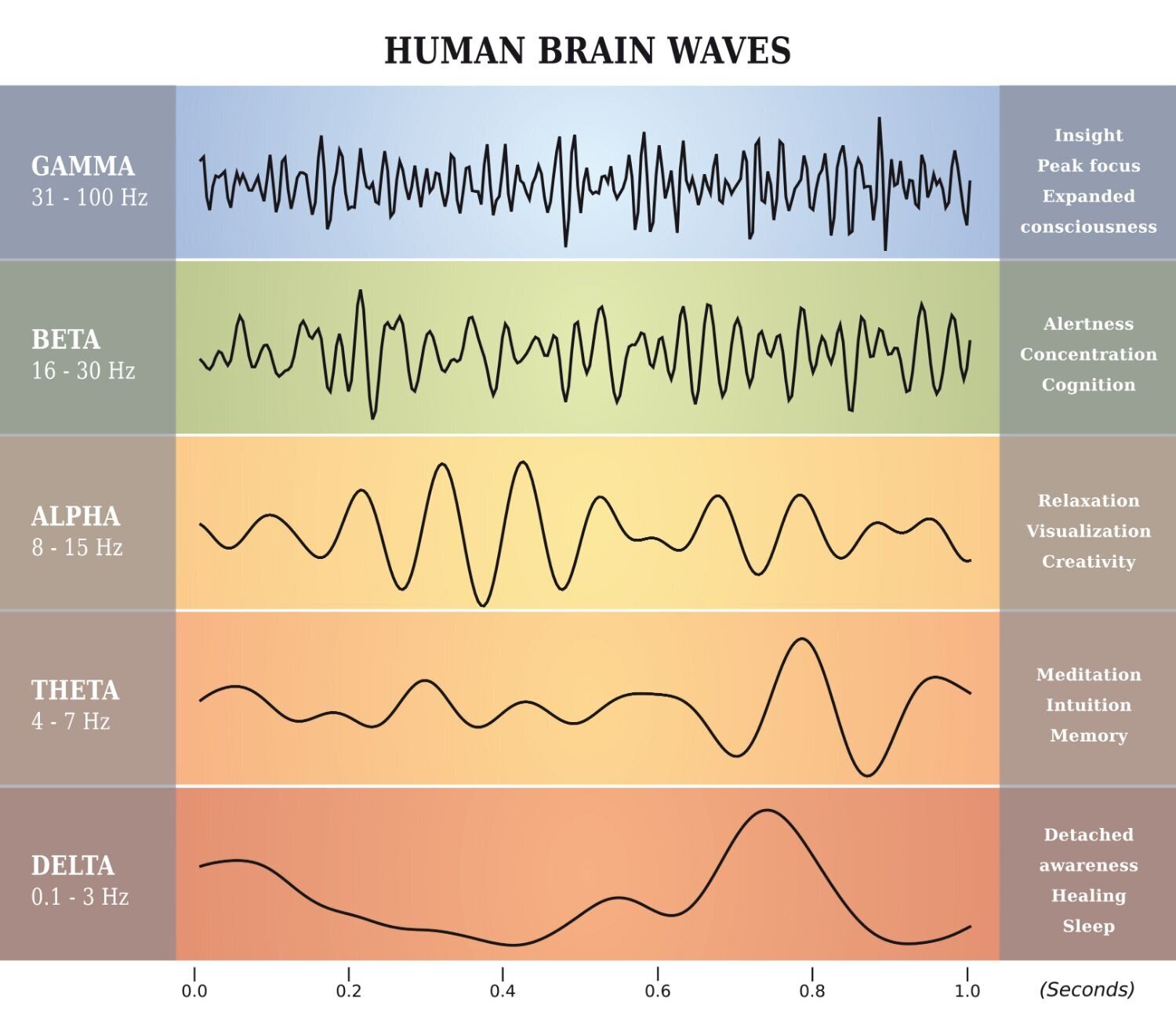
There are 5 main categories of brain waves.
- Delta Waves (0.5-4 Hz): Delta waves are the slowest brain waves, typically associated with deep sleep, unconsciousness, and dreamless sleep. Delta waves can also be observed in individuals with certain brain injuries or neurological conditions.
- Theta Waves (4-8 Hz): Theta waves are present during light sleep, meditation, relaxation, and deep creative or imaginative states. These waves usually associated with memory formation, learning, and spatial navigation.
- Alpha Waves (8-13 Hz): Alpha waves are prominent during relaxed wakefulness, often associated with a state of calmness, alertness, and light meditation. In situations when the eyes are closed but the individual remains awake and not actively engaged in mental tasks, observers can notice delta waves.
- Beta Waves (13-30 Hz): Beta waves are characteristic of active wakefulness, often associated with focused attention, alertness, problem-solving, and cognitive tasks. Also observed during stress, anxiety, and intense mental activity.
- Gamma Waves (30-100 Hz): Gamma waves are the fastest brain waves, often associated with high-level cognitive processes, information processing, perception, and consciousness. Additionally they also play a role in integrating sensory information and coordinating brain activity across different brain regions.
Lets Summarize one more time…..
| Beta waves | Associated with active, waking states and cognitive tasks. |
| Alpha waves | Present during relaxed, wakeful states, such as meditation or daydreaming. |
| Theta waves | Occur during light sleep, deep meditation, or creative thinking. |
| Delta waves | Typically observed during deep sleep or in cases of brain injury. |
| Gamma waves | Linked to cognitive processes like memory formation and perception. |
How do Brain Waves Communicate?
EEGs measure brain waves, which reflect synchronized electrical activity generated by masses of communicating neurons. While brain waves themselves don’t directly communicate information in the way neurons communicate, they do serve as reflection of neural activity and helps us identify states of brain function. Following are some ways how brain waves communicate.
01
Synchronization and Communication
When neurons fire together in large numbers, they produce synchronized electrical activity, which manifests as brain waves. This synchronization is crucial for communication within the brain. Neurons communicate with each other through electrical impulses and neurotransmitters. The patterns of brain waves reflect the coordinated firing of neurons in different brain regions.
02
Information Processing
While brain waves themselves don’t convey specific information, their patterns and frequencies correlate with different states of consciousness, attention, and cognitive processing. For example, during focused attention, beta waves may dominate, while during relaxation, alpha waves may be more prominent. Additionally, certain tasks or mental states may be associated with specific patterns of brain wave activity.
03
Neural Networks
Brain waves reflect the activity of interconnected groups of neurons, known as neural networks, which process specific types of information or perform certain functions. These networks allow different brain regions to communicate and coordinate their activities, enabling complex cognitive processes.
04
Clinical Applications
Brain wave analysis has various clinical applications, such as diagnosing neurological disorders, monitoring brain function during surgery, and assessing brain injury or coma states. Researchers also use brain wave data to study cognitive processes, emotions, and consciousness.
Let us help you
Retrain your Brian
Break the unhealthy patterns!!
Complimentary Advice • Round-the-Clock Support

